Half Wave Rectifier
2 in stock
Click Here to Download the Circuit Diagram of “Half Wave Rectifier”
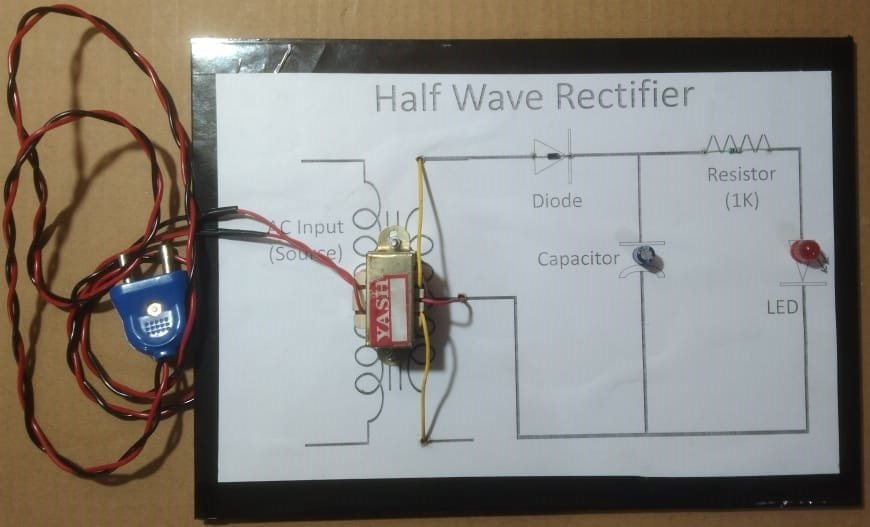
A half-wave rectifier converts AC voltage to DC voltage using a single diode. In this project, connect an AC voltage source to the input terminals of a diode, with the anode connected to the positive terminal of the AC source and the cathode to a load resistor. The diode allows current to pass only during the positive half of the AC cycle, blocking the negative half. The output across the load resistor will be a pulsating DC signal, representing only the positive half of the input AC waveform. This setup demonstrates the basic principle of rectification and provides insight into the function of diodes in power supplies.
₹442.50 ₹649.00 (Incl. GST)
2 in stock
Half Wave Rectifier Project
A half-wave rectifier is an electronic circuit designed to convert alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC) by allowing only one half-cycle of the AC voltage to pass through, effectively blocking the other half. This process is fundamental in power supply units and various electronic devices.
Components Used:
- Transformer: Steps down the high AC voltage to a lower, manageable level suitable for rectification.
- Diode: Allows current to flow in a single direction, facilitating the rectification process by permitting only the positive half-cycles of AC to pass through.
- Resistor: Limits the current flow within the circuit, protecting components from potential damage due to excessive current.
- Capacitor: Smooths the pulsating DC output by filtering out voltage ripples, resulting in a more stable DC voltage.
- LED (Light Emitting Diode): Acts as an indicator, illuminating when current flows through the circuit, thereby confirming the presence of output voltage.
Working Principle:
During the positive half-cycle of the AC input, the diode becomes forward-biased, allowing current to pass through the load resistor. Simultaneously, the capacitor charges up to the peak voltage. In the negative half-cycle, the diode is reverse-biased, blocking current flow. The charged capacitor then discharges through the load, providing a continuous DC output. The LED lights up during the positive half-cycle, indicating active current flow.
Applications:
- Signal Demodulation: Extracts the audio signal from modulated radio signals.
- Power Supply Circuits: Provides DC voltage for low-power devices and appliances.
- Pulse Generation Circuits: Generates DC pulses for timing and control applications.
Advantages:
- Simplicity: Comprises a straightforward design with minimal components, making it easy to construct and understand.
- Cost-Effective: Requires fewer components, leading to lower manufacturing costs.
Limitations:
- Inefficiency: Utilizes only half of the AC waveform, resulting in significant power loss and reduced efficiency.
- High Ripple Factor: Produces a pulsating DC output with substantial ripples, necessitating additional filtering for applications requiring smooth DC voltage.
- Low Output Voltage: Delivers a lower average output voltage compared to full-wave rectifiers.
Conclusion:
While half-wave rectifiers are suitable for simple, low-power applications due to their ease of implementation and cost-effectiveness, they are generally inadequate for powering sensitive electronic equipment. The inherent inefficiency and high ripple content limit their use in scenarios where a stable and smooth DC output is essential. In such cases, more efficient rectification methods, like full-wave rectifiers, are preferred.
| Weight | 0.00 kg |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 0.00 × 0.00 × 0.00 cm |
You may also like…
-
B.Tech Diploma Mini Projects
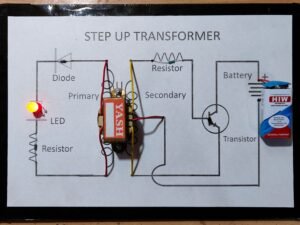
Step Up Transformer
A Step-Up Transformer increases voltage from a lower to a higher level by using two coils: the primary and secondary. The secondary coil has more turns, producing a higher output voltage. This project demonstrates its role in power transmission, reducing energy losses, and applications in electrical devices like microwaves and X-rays.
SKU: Step Up Transformer