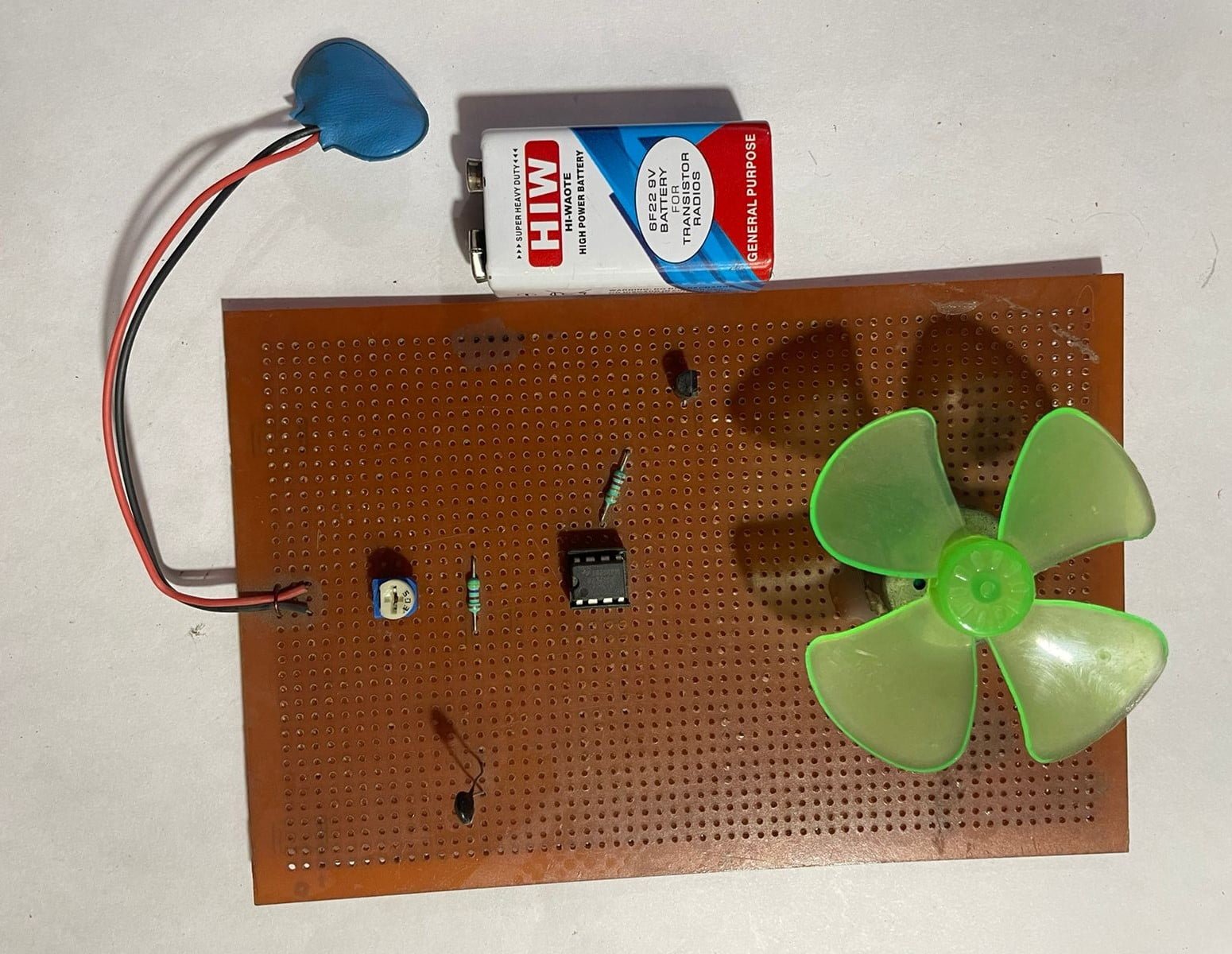
Temperature Controlled DC Fan
5 in stock
₹442.50 ₹613.60 (Incl. GST)
5 in stock
Temperature Controlled DC Fan
A Temperature Controlled DC Fan is an innovative circuit designed to manage fan speed in response to temperature fluctuations, optimizing cooling efficiency and energy consumption. This type of circuit is commonly used in electronics cooling systems, computer cases, and various temperature-sensitive applications to maintain a stable operating environment.
How It Works
The core components of a Temperature Controlled DC Fan circuit include a DC fan, a temperature sensor, and a control unit, typically an operational amplifier (op-amp) or a microcontroller. Here’s a breakdown of how each component contributes to the circuit:
- Temperature Sensor: This device measures the ambient temperature and converts it into an electrical signal. Common temperature sensors include thermistors, LM35, or DHT11. The sensor’s output voltage changes with temperature variations, providing a continuous temperature reading.
- Control Unit: The control unit interprets the temperature data from the sensor and determines the appropriate fan speed. In analog circuits, this might be achieved using an op-amp to compare the temperature signal with a reference voltage. In digital circuits, a microcontroller can be programmed to handle this task, offering more flexibility and additional features.
- DC Fan: The fan’s speed is adjusted based on the control signal from the control unit. This is typically managed using a Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) signal, where the fan speed is proportional to the duty cycle of the PWM signal. The fan spins faster or slower depending on the temperature to provide the required cooling.
Applications
Temperature Controlled DC Fans are used in a variety of applications to enhance efficiency and protect sensitive components:
- Computers and Electronics: They prevent overheating of components by adjusting fan speeds based on the internal temperature, thereby improving performance and longevity.
- HVAC Systems: Used in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems to regulate temperature and ensure optimal air circulation.
- Battery Management: In battery-powered devices, they manage temperature to prevent overheating and extend battery life.
Advantages
- Energy Efficiency: By adjusting the fan speed based on temperature, the circuit reduces unnecessary power consumption, leading to lower energy costs.
- Enhanced Cooling: Ensures that cooling is provided only when needed, maintaining the desired temperature effectively.
- Extended Component Life: Prevents overheating, which can prolong the life of electronic components and systems.
Conclusion
The Temperature Controlled DC Fan circuit is a practical solution for managing temperature and enhancing the efficiency of cooling systems. By dynamically adjusting fan speed in response to temperature changes, it ensures optimal performance and energy efficiency across a range of applications.
| Weight | 0.00 kg |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 0.00 × 0.00 × 0.00 cm |