Diode as a Switch
5 in stock
Click Here to Download the Circuit Diagram of “Diode as a Switch”
₹295.00 ₹531.00 (Incl. GST)
5 in stock
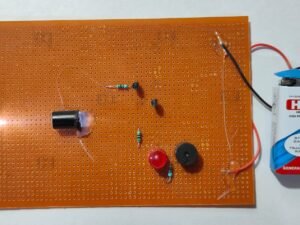
The Diode as a Switch project demonstrates how a diode can be used to control the flow of current in a circuit, functioning similarly to a switch. This project illustrates the diode’s fundamental role in electronics, showcasing its ability to permit current flow in one direction while blocking it in the reverse direction.
Project Overview
Objective: To use a diode to control the flow of current in a circuit, effectively acting as an on-off switch.
Materials Needed
- Diode: 1N4148 or similar
- Resistor: 220 ohms (for current limiting)
- LED: Light Emitting Diode
- Battery: 9V battery or any suitable power source
- Breadboard and Jumper Wires: For circuit assembly
Steps to Build the Circuit
- Understand the Diode’s Function: A diode is a semiconductor device that allows current to flow in one direction only. When forward-biased (positive voltage on the anode and negative on the cathode), it conducts electricity. When reverse-biased (positive voltage on the cathode and negative on the anode), it blocks current flow.
- Prepare the Circuit Components: Place the diode, LED, and resistor on the breadboard. Ensure you correctly identify the anode and cathode of the diode and LED. The anode is the longer leg of the LED and the end of the diode with the positive sign.
- Connect the Diode: Insert the diode into the breadboard. Connect the anode (positive end) of the diode to the positive terminal of the battery. Connect the cathode (negative end) to one end of the resistor.
- Attach the Resistor: Connect the other end of the resistor to the anode of the LED. This resistor limits the current through the LED, preventing it from burning out.
- Connect the LED: Connect the cathode of the LED to the negative terminal of the battery.
- Power the Circuit: Once all connections are made, power the circuit by connecting the battery. The LED should light up if the diode is forward-biased. If the diode is reverse-biased, the LED will remain off.
Testing and Observation
- Forward-Biased Diode: When the diode is correctly oriented (forward-biased), it allows current to flow from the battery through the LED, causing the LED to light up. This demonstrates the diode acting as a closed switch, allowing current to pass through.
- Reverse-Biased Diode: Reversing the diode’s orientation will block current flow. The LED will not light up, demonstrating the diode acting as an open switch. This shows how the diode prevents current flow in the reverse direction.
Practical Applications
- Diode as a Protection Device: In circuits, diodes are often used to protect against reverse polarity, ensuring that current flows only in the desired direction.
- Signal Routing: Diodes can be used in signal routing applications where controlling the direction of current flow is crucial.
By completing this project, you will gain practical experience with the diode’s rectifying properties and its utility in electronic circuits as a switch. This simple yet effective demonstration lays the groundwork for more complex circuit designs involving diodes and other components.
| Weight | 0.00 kg |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 0.00 × 0.00 × 0.00 cm |