DC Motor Speed and Direction Control
1 in stock
DC Motor Speed and Direction Control
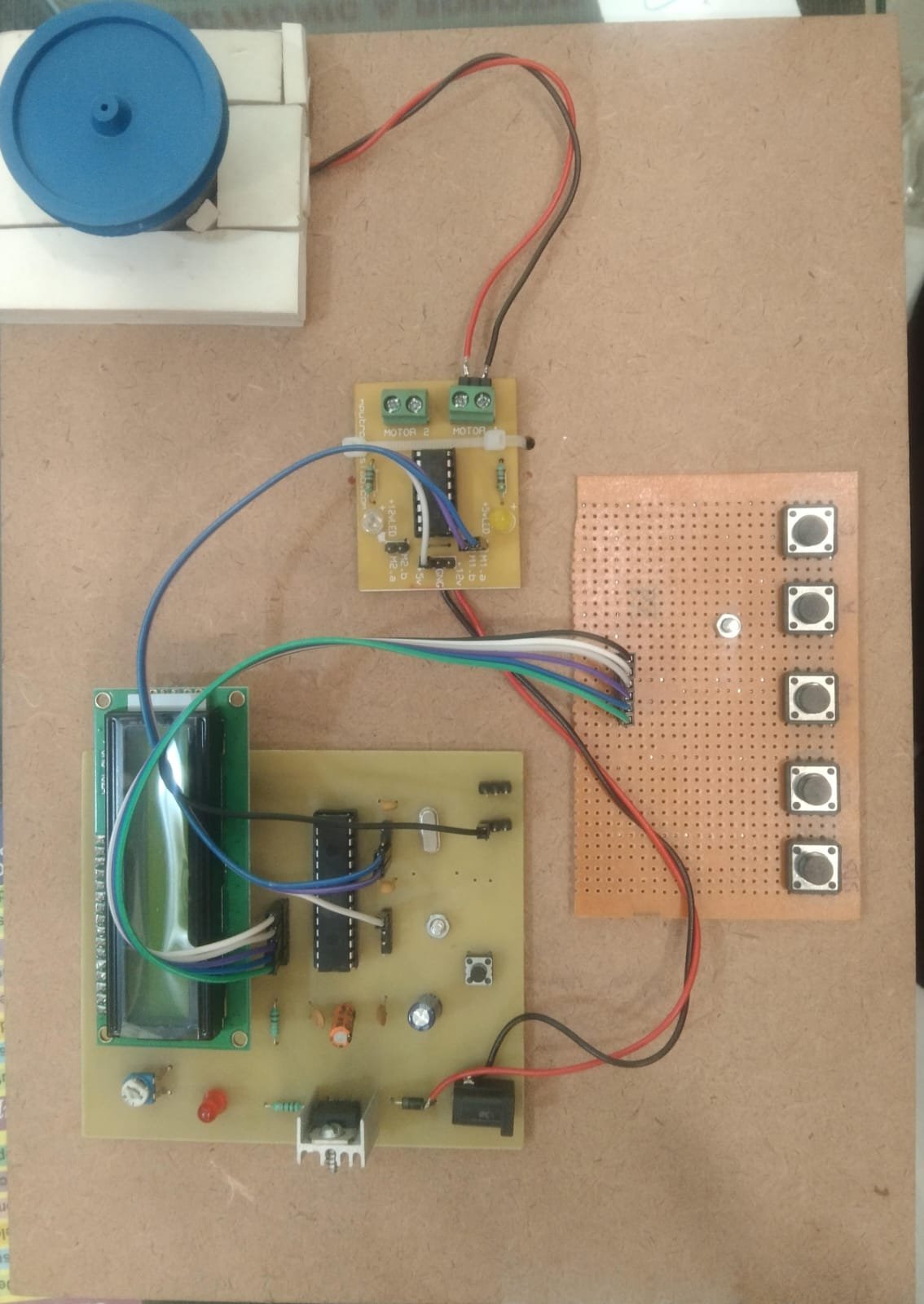
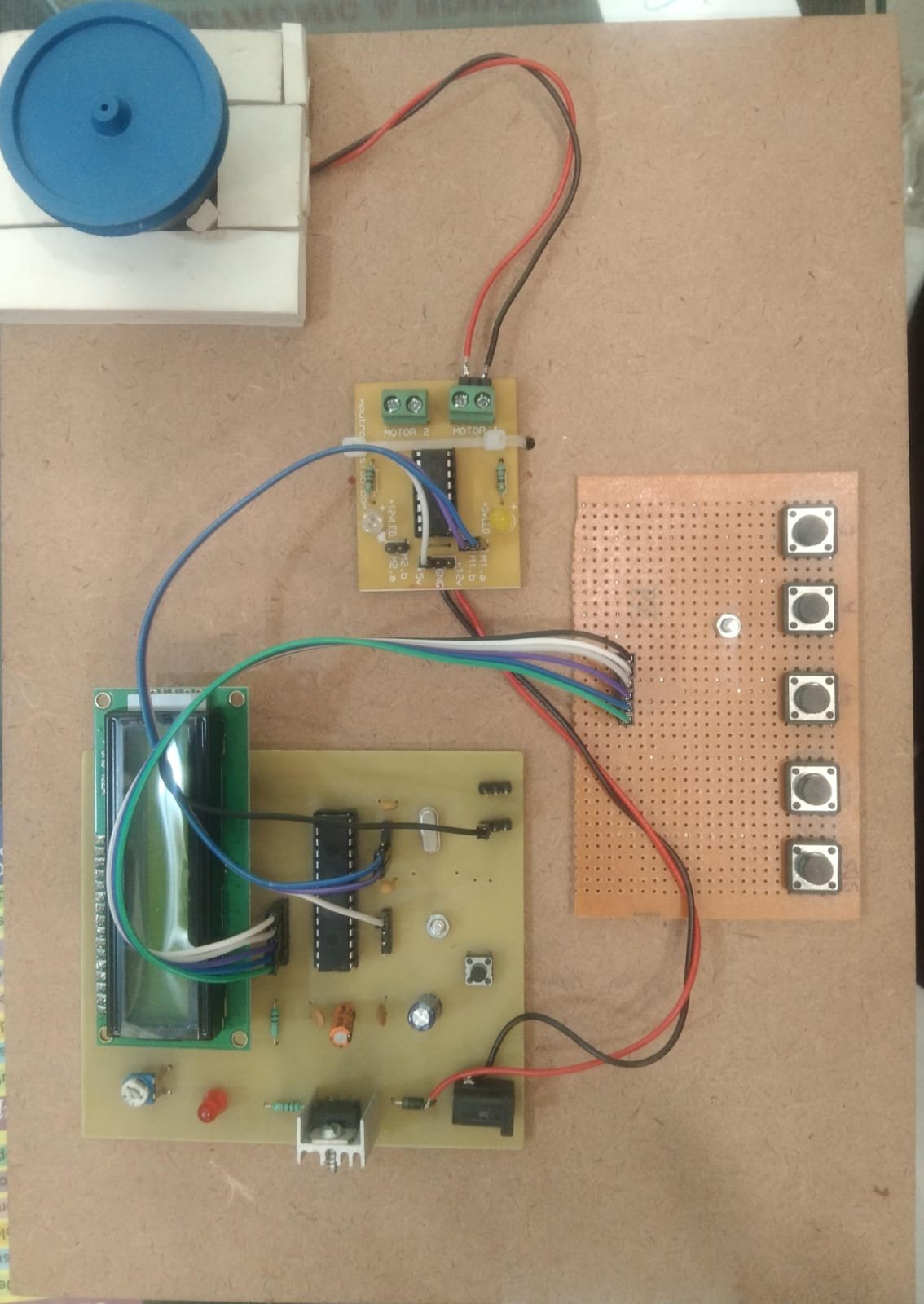
Controlling the speed and direction of a DC motor is essential in robotics, automation, and various electronic systems. This project demonstrates how to control a DC motor’s speed and direction using a microcontroller (like Arduino), an H-bridge motor driver (such as L298N or L293D), and PWM (Pulse Width Modulation).
₹3,481.00 ₹4,130.00 (Incl. GST)
1 in stock
DC Motor Speed and Direction Control
Controlling the speed and direction of a DC motor is essential in robotics, automation, and various electronic systems. This project demonstrates how to control a DC motor’s speed and direction using a microcontroller (like Arduino), an H-bridge motor driver (such as L298N or L293D), and PWM (Pulse Width Modulation).
⚙️ Working Principle
-
Speed Control using PWM:
-
PWM is a technique used to vary the average voltage supplied to the motor by switching it ON and OFF rapidly.
-
The higher the duty cycle (ON time), the faster the motor rotates.
-
Arduino can generate PWM signals using the
analogWrite()function.
-
-
Direction Control using H-Bridge:
-
An H-bridge is an electronic circuit that allows voltage to be applied across a load in either direction.
-
It consists of 5 switches/transistors; by changing their states, the current flow through the motor can be reversed.
-
L298N and L293D motor drivers make this easy by providing input pins to control direction and enable pins for speed control.
Typical Connections:
-
IN1 and IN2 control direction (e.g., IN1 HIGH & IN2 LOW = Forward)
-
ENA (Enable pin) controls speed using PWM
-
Arduino takes user input (e.g., from a potentiometer or buttons) and adjusts motor behavior accordingly
💡 Applications:
-
Robotics (line follower, obstacle avoidance)
-
Conveyor belts
-
Smart home devices (curtains, fans)
-
Electric vehicles
✅ Advantages:
-
Precise control over motion
-
Easily programmable and scalable
-
Can be expanded for dual motors or remote control
-
-